The Life-Saving Impact of How Organ Transport Saves Lives
Organ transport ensures donated organs stay viable for transplantation, directly impacting survival rates. This article explores how organ transport saves lives through efficient transport methods, preservation techniques, and the teamwork behind successful transplants.
Key Takeaways
Organ transport is crucial for the viability of donated organs, directly impacting the success of transplants and potentially saving multiple lives from a single donor.
Technological advancements and efficient methods of organ preservation and transport, such as hypothermic machine perfusion and advanced aerial vehicles, are essential for improving transplant outcomes and organ viability.
Coordination among healthcare professionals and logistics teams is vital for timely organ transport, which is necessary to minimize the risk of deterioration and increase the likelihood of successful transplants.
The Critical Role of Organ Transport
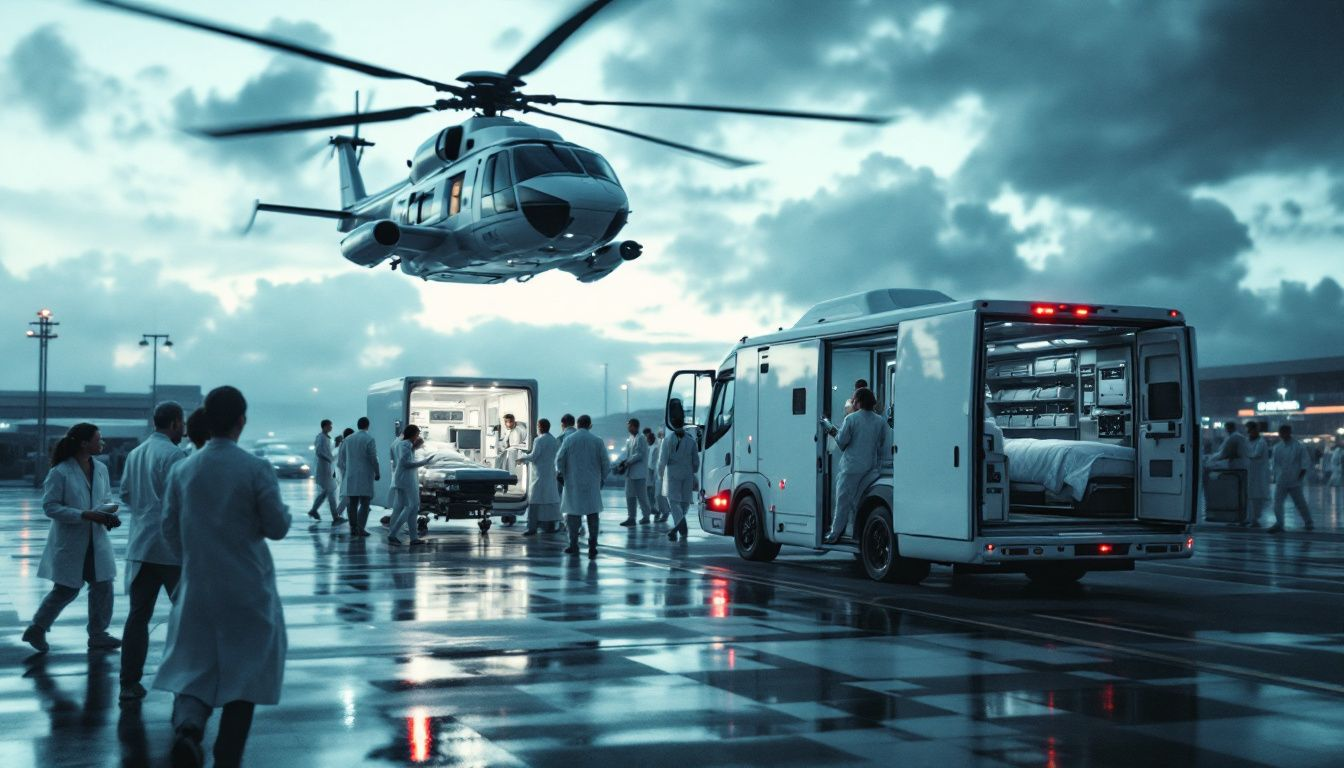

Organ transport is the lifeline that bridges the gap between organ donors and transplant recipients. Its main function is to keep organs viable for transplantation, greatly influencing the procedure’s success. Efficient organ transport can drastically reduce transplant complications, often making the difference between life and death.
Several factors determine the success of organ transport, such as distance, transport method, and timing of organ retrieval. These elements ensure the organs reach their destinations in optimal condition. Successful organ donation requires collaboration among healthcare professionals like nurses, transplant coordinators, and physicians, who work tirelessly to identify donors and facilitate timely donations.
A single organ donor can save multiple lives, with each donor’s organs potentially benefiting several patients in need, whether from a deceased or living donor or living donors. This underscores the immense demand for organ donation, evidenced by institutions like IU Health, performing over 500 transplants annually.
Despite advancements, a significant issue remains the global shortage of available organs, with only about 10% of the need for transplants being met worldwide. Past developments in organ transport have improved survival rates for transplant recipients, highlighting its life-saving impact.
Organ Retrieval and Preparation
The journey of an organ from donor to recipient begins in the operating room, where a dedicated surgical team retrieves the organs from a donor. This delicate process requires meticulous care and precision to ensure organs are suitable for transplant surgery. Before recovery, coordinated efforts stabilize donor physiological conditions, ensuring organs remain in optimal state.
Once retrieved, organs are washed with a cold preservation solution to remove any remaining blood, a crucial step for transport preparation. They are then placed in sterile containers and stored on wet ice to maintain viability during the journey to the transplant site. Organ procurement is a race against time; the longer organs are outside a body, the higher the risk of deterioration.
Recent innovations have significantly improved donor organ recovery and preservation, addressing the supply-demand imbalance. Such advancements optimize organ use, allowing more patients on the waiting list to receive life-saving transplants.
The entire process, from retrieval to preparation, is a testament to the dedication and expertise of the medical professionals involved.
Organ Preservation Techniques
Maintaining the viability of organs during transport is a scientific and logistical challenge. Cooling is the primary method to slow metabolic activity, essential for preserving transported organs. Temperature control is vital as it directly impacts transplantation success.
Static cold storage, especially for kidneys, is the most common preservation method. This technique involves placing organs in a cold preservation solution and storing them on ice. However, newer methods like hypothermic machine perfusion, which circulates preservation solutions continuously, enhance organ viability. Preservation solutions maintain cellular integrity by mitigating ischemia effects.
The cold ischemic times vary significantly by organ, with kidneys tolerating up to 24 hours, while hearts are limited to just 4-6 hours. Reducing transportation time minimizes ischemic tissue damage.
Emerging technologies like machine perfusion and targeted preservation solutions have expanded organ viability and improved outcomes for marginal organs. Techniques like normothermic regional perfusion (NRP) and ex vivo normothermic machine perfusion enhance organ viability and reduce discard rates.
Speed and Efficiency in Organ Transport
In the realm of organ transplantation, time is of the essence. Certain organs, like hearts and lungs, have strict transplant timeframes. For instance, hearts and lungs need to be transplanted within about four hours post-retrieval. Fast transportation increases the chance of a successful transplant by reducing travel times.
Innovative methods like Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) could significantly shorten transport duration, ensuring organ viability. Temperature control during transport is also vital for preserving organ viability.
Speed and efficiency in organ transport are paramount to saving lives through successful transplants.
Monitoring During Transport
Careful monitoring during organ transport, such as with tracking systems for organ transports, is essential to ensure they remain in optimal condition. Temperature is closely monitored to keep the organs within a range that maintains their viability. This meticulous attention to detail helps prevent any damage that could compromise the success of the transplant.
Efforts throughout transportation aim to avoid healthy organ damage, ensuring they arrive in the best possible state for transplantation. Such careful monitoring preserves the life-saving potential of each organ.
Did you know that you can get from Manhattan to JFK in under 5 minutes without driving?
Blade offers seamless helicopter transfers from our West 30th Street Lounge in Manhattan to JFK Airport in just 5 minutes from $195 per seat.
Skip the traffic and ditch the stress with Blade's year-round airport service.

Coordination and Teamwork
Successful organ transport relies heavily on coordination and teamwork among medical and logistics professionals. Certified couriers transport organs, tracked using monitoring devices to ensure safety. This intricate process requires seamless communication and collaboration among all parties.
Advancements in organ allocation systems enhance access for patients in low donation areas, ensuring broader sharing of donor organs. Tissue donation is being explored to improve donor-recipient matching and adapt immunosuppressive therapies based on patient response.
Coordination and teamwork are the backbone of successful organ matching and transport logistics and the transplant team involved in transplantation.
The Role of Technology in Organ Transport
Technological advancements have revolutionized organ transport efficiency, ensuring organs remain viable for transplantation. One significant development is the use of advanced aerial vehicles, reducing reliance on ground transport and avoiding congestion and delays. This innovation is particularly beneficial for quickly transporting organs over long distances.
Kidney perfusion machines, another technological advancement, enable remote monitoring during transportation, enhancing organ viability for kidney transplant.
Integrating technology in organ transport is a game-changer, improving transplant success rates and saving more lives.
Success Stories: Lives Saved Through Efficient Organ Transport
Real-life success stories illustrate the profound impact of efficient organ transport. For example, Audrey, a baby diagnosed with total liver failure at just three months old. Audrey urgently needed a liver transplant to survive.
Placed on the transplant list on July 7, 2018, Audrey received a call for a donor liver just 13 days later. This swift process ensured Audrey received the life-saving transplant she needed, highlighting timely organ transport’s critical role.
Stories like Audrey’s inspire hope and underscore the life-saving potential of organ donation and transplantation.
Challenges in Organ Transport
Despite advancements and successes, challenges in organ transport remain. A significant challenge is the risk of organ rejection post-organ transplant, necessitating lifelong immunosuppressive drugs. These drugs can lead to severe side effects and complications, making post-transplant care a delicate balancing act.
The global shortage of available organs is another major challenge, with only about 10% of transplant needs being met worldwide. This shortage underscores the importance of increasing organ donation and improving transport methods. Addressing these challenges is crucial for long-term organ transplantation success.
Did you know that you can get from Manhattan to JFK in under 5 minutes without driving?
Blade offers seamless helicopter transfers from our West 30th Street Lounge in Manhattan to JFK Airport in just 5 minutes from $195 per seat.
Skip the traffic and ditch the stress with Blade's year-round airport service.

The Future of Organ Transport
The future of organ transport holds exciting possibilities. Rapid transport methods can enhance organ allocation logistics by broadening the geographic area for retrieval. This expansion could significantly increase organ availability for patients in need.
Ongoing research into therapies that could re-educate the immune system to accept transplanted organs offers hope for reducing immunosuppressant reliance. Such advancements could revolutionize organ transplantation, making it safer and more effective for recipients.
The future of organ transport is bright, with the potential to save more lives and improve transplant recipients’ quality of life.
Bottom Line: How Organ Transport Saves Lives
In summary, organ transport is a critical component of organ transplantation, ensuring that organs remain viable and reach their recipients in time. The intricate process involves careful coordination, advanced preservation techniques, and the use of innovative transport methods. Despite the challenges, the advancements in technology and the dedication of medical professionals continue to save lives.
The future of organ transport looks promising, with ongoing research and technological advancements paving the way for even greater success. By understanding and supporting organ donation and transport, we can contribute to saving lives and giving patients a second chance at life.
FAQs about How Organ Transport Saves Lives
Why is organ transport so vital in transplantation?
Organ transport is vital in transplantation because it preserves the viability of organs, directly influencing the success of the procedure and enhancing survival rates for recipients. Timely and efficient transport minimizes potential complications associated with organ degradation.
How are organs preserved during transport?
Organs are preserved during transport primarily by cooling methods to slow metabolic activity, often placed in cold preservation solutions and kept on ice or through advanced techniques such as hypothermic machine perfusion. This approach ensures the organs remain viable until transplantation.
What role does technology play in organ transport?
Technology plays a crucial role in organ transport by enhancing speed and efficiency through advanced aerial vehicles, and by utilizing kidney perfusion machines and improved preservation methods that ensure organ viability. These innovations significantly improve the chances of successful transplants.
What are the challenges faced in organ transport?
The primary challenges in organ transport include the risk of organ rejection, the necessity for lifelong immunosuppressive therapy, and the global shortage of donor organs. Effectively addressing these issues is essential for enhancing the success of organ transplantation.
How does coordination and teamwork contribute to successful organ transport?
Coordination and teamwork are essential for successful organ transport, as they ensure that medical professionals, transport services, and allocation systems work together effectively to deliver organs in optimal condition. This collaborative effort ultimately enhances the chances of successful transplants and improves patient outcomes.
Disclaimer:
Please be aware that the content on this page has been generated by using artificial intelligence language models and may contain errors, inconsistencies, or outdated information. It is provided as-is without any warranties or guarantees of accuracy. We strongly recommend using this content as a starting point for further research. We disclaim any liability for damages or losses resulting from the use or reliance on this content.